News | May 31, 2024
Economic growth and innovation in Albania: an in-depth look at ProSEED 2.0 and EU4Innovation initiatives


In March 2024, the Practitioners' Network for European Development Cooperation visited Albania to foster European integration and cooperation within the country and the region.
The visit provided an opportunity for Network Members to discuss and present effective examples of joint implementation. The goal was to develop strategies for Working Better Together as part of a Team Europe approach and to enhance and coordinate the technical offer from Team Europe in Albania and the wider Balkans. The focus areas included alignment with the EU acquis, good neighborly relations, the green agenda, sustainable connectivity, and the digital economy and society.
As an example of education, innovation, and economic growth, this interview with project managers from GIZ involved in the ProSEED 2.0 and EU4Innovation projects provides insights into the cooperative approach of these initiatives.
Can you provide an overview of the ProSEED 2.0 and EU4INNOVATION projects you are implementing in Albania?
ProSEED 2.0 stands for “Sustainable Economic and Regional Development, Employment Promotion and Vocational Education and Training”; this is a programme funded by Federal Republic of Germany and implemented in partnership with the Government of Albania/Ministry of Economy, Culture and Innovation. The programme’s objective is that “both the economic development and the employment situation in Albania are improving throughout the country, and a special focus is on green and digital skills advancement as well as business processes”.
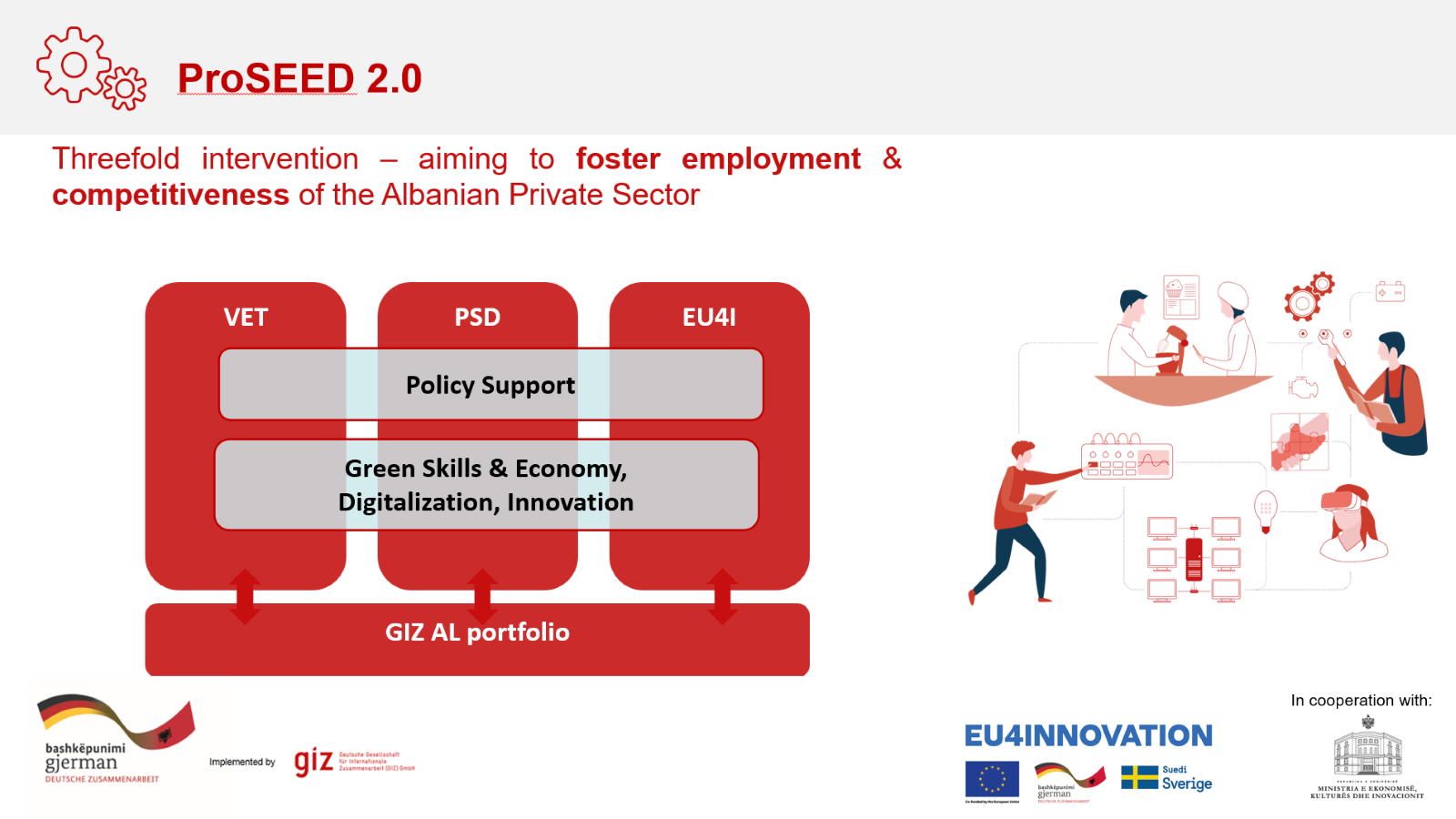
Figure 1:ProSEED 2.0 and EU4Innovation programme set-up.
ProSEED 2.0 joins forces with EU4Innovation, a co-funded project. EU4Innovation is a multi-donor Action that supports the Government of Albania (GoA) in the field of economic development, by accelerating the country’s economic transformation into an innovation-driven and knowledge-based one, leveraging on Albania’s human capital, entrepreneurial and research potential, thereby increasing its competitiveness.
What are the projects´ main objectives and goals?
The main objective of ProSEED 2.0 is to support the GoA in fostering economic growth, creating job opportunities, supporting SMEs and startups, enhancing innovation and entrepreneurship, and promoting sustainable development. The project operates in three main components, and the respective goals are:
- The vocational education and training (VET) system is improved, VET qualifications and curricula is modernised integrating digital and green elements. Approximately 5,000 people have gained green and digital skills via non-formal and formal qualification measures.
- Support is provided to 800+ MSMEs with a focus on improving their competitiveness by digitalising their business processes and introducing green business elements. Five new business development services are established at national, regional or local level.
- Policy development support is provided to the line ministry(ministries) and subordinate institutions to develop new employment-related strategies or action plans that include digital or green economic aspects.
Additionally, EU4Innovation’s specific objective is the “Increased maturity and exposure of the Albanian start-up and innovation ecosystem and its stakeholders”. his objective is pursued through activities in four main outputs:
- Capacity development addressing the start-up and innovation ecosystem. New public and private actors are encouraged to enter the Albanian start-up and innovation ecosystem and complement /expand current services.
- Improving access to finance for Albanian start-ups and Innovation Support Organizations (ISOs). This is a shared responsibility between GIZ & Sida.
- Promoting and implementing the quadruple helix approach, which is indispensable for driving innovation and gaining access to Horizon Europe Funds. This approach involves collaboration between academia, government, industry, and civil society.
- Promoting Albania as a start-up and innovation ecosystem and destination for international and domestic innovators and entrepreneurs.
How many European Development Cooperation organisations are participating in the projects?
While ProSEED 2.0 is a bilateral programme implemented by GIZ Albania, and the sole Commissioning Party is the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ); EU4Innovation is funded by the European Union, with additional support from the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), and the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida). The programme is implemented by GIZ Albania and the Swedish Embassy Tirana.
What is the added value brought by each organization participating in the ProSEED 2.0 and EU4INNOVATION projects?
GIZ is a trusted partner of the Government of Albania for transformative change, focusing mainly in four core areas in Albania: Economic resilience, Climate adaptation, Livable cities, EU Integration. In the case of multi-donor actions such as EU4Innovation, GIZ is implementing the project in collaboration with Sida, specifically co-implementing output 2 of EU4I “access to finance”. The Challenge Fund is a competitive financing facility used to address the issue of access to finance for innovative companies at all stages of development (idea, validation, growth and scale-up). The value of joint efforts of various organisations is impactful when complementary actions are taken. A very good example, from phase 1 of EU4Innovation joint efforts of GIZ and Sida is the Innovation Factory at Polis University. As part of its mission to strengthen Albania's innovation and start-up ecosystem, the EU4Innovation multi-donor-action implemented by GIZ and Sida, supported Albanian Universities in their endeavor to become more entrepreneurial. The Action also provided demand-driven consultancy and financial support to selected universities, with UPolis being among the most prominent examples. The coordinated technical offer of GIZ and Sida for this education institution was a highlight of the “Working Better Together” as part of a Team Europe approach in Albania.
How do the projects collaborate with other organisations or stakeholders involved in development activities in Albania?
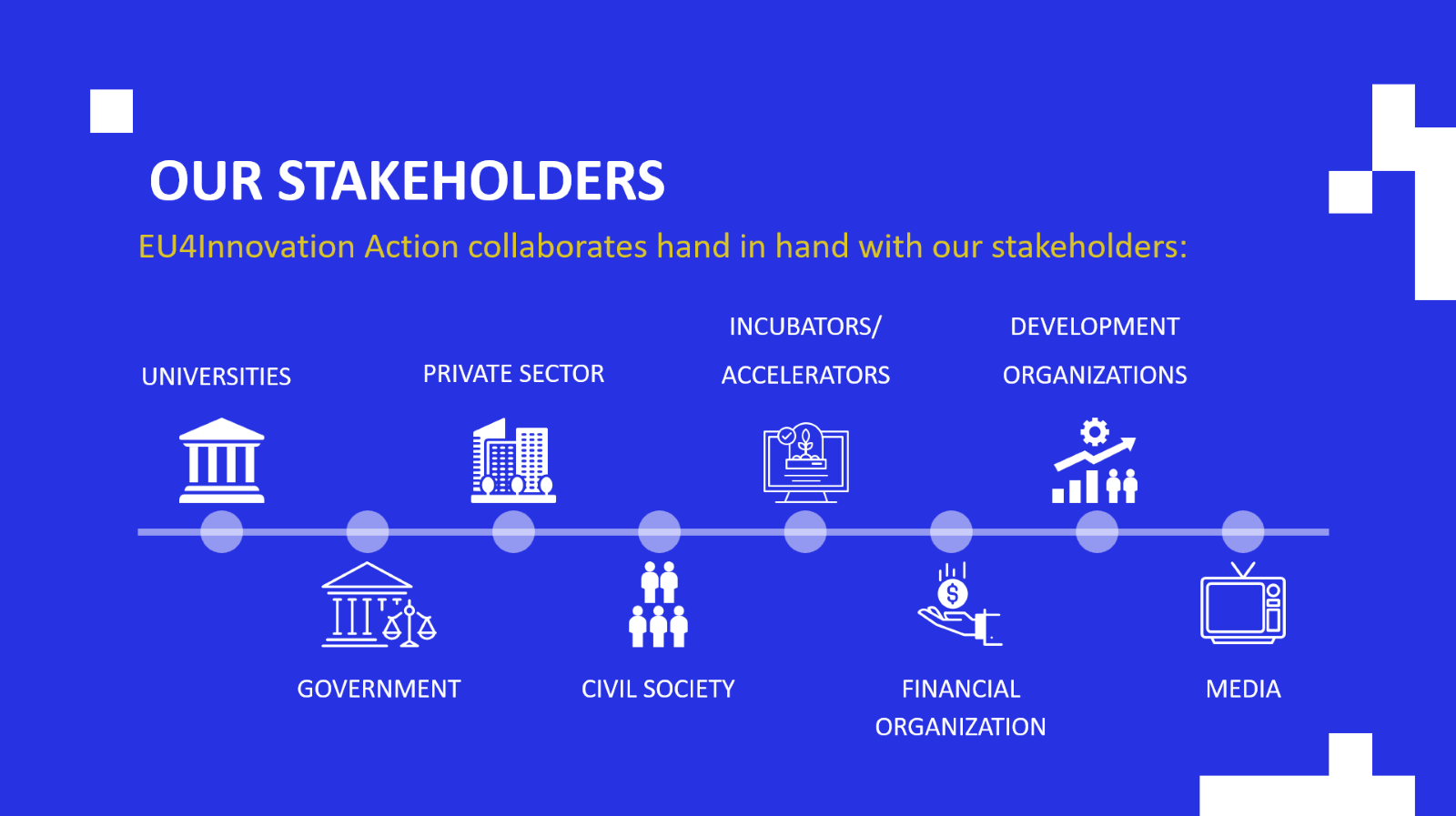
Figure 2:EU4Innovation stakeholder map.
The EU and Germany work together as Team Europe with the Government of Albania to drive sustainable economic growth and creation of more jobs. Team Europe in Albania impresses through its strong presence with GIZ playing a pivotal role. Lighthouse projects on innovation (11.75 million EUR multi-donor Action between Europe, Germany & the Kingdom of Sweden) and the circular economy (co-finance of 10 million EUR) that drive innovation, start-ups, innovative, green & circular business.
Besides the EU delegation to Albania, GIZ Albania works closely with Swish Development Cooperation, a strong development partner active in VET, employment, private sectors, and development banks, such as KfW, which is providing essential complementary financial cooperation in the VET sector.
Joint partners in these initiatives include ministries such as: MoECI, MoEI, MoTE, MoES and government agencies such as NAES, NAVETQ, AIDA, NASRI, etc. Both programmes collaborate closely with other organisations and stakeholders involved in development activities in Albania, including, CSOs, academic institutions, and the private sector. This collaboration ensures coordination, synergy, and maximises the project's impact.
How do the projects contribute to broader development goals or priorities in Albania?
We would like to respond to this question, by linking it to EU integration of Albania, and the fact that GIZ is a trusted partner of GoA towards EU integration. Albania is fully committed to conduct successful negotiations with the EU. The necessary structures are set up to complete the screening process, work on benchmarks, formulate negotiating positions, etc.
The Government has set an ambitious strategic framework for EU membership NSDEI 2023 – 2030, National Program for Accession to the European Union 2024-2030 and the associated National Plan for European Integration to ensure alignment of reforms, policies, and legislation with EU standards. Efforts are being made to carry forward the necessary reforms and boost policy and regulatory processes in an inclusive and participatory way. Support to accelerate integration in specific areas has been provided, such as concrete initiatives in the framework of the EU’s Growth Plan that opens certain areas of the EU single market with tangible benefits to citizens prior to accession.
GIZ, via ProSEED and EU4Innovation, supports building capacities of the Public Administration to manage the process of EU accession at all levels (planning, implementation and monitoring). GIZ provides EU-compliant policy and strategic advice to create prospects for employment through qualification and economic development, focusing on green skills and green businesses, strengthening the start-up & innovation ecosystem, as well as fostering the further digitalisation in VET and PSD, and the entire knowledge-based and innovation driven economy. As an example, ‘EU4Innovation’ project, which follows a demand-driven approach, especially in the case of the political partners/government institutions responsible for delivering policy inputs in the field of innovation and start-up promotion. Some excellent examples are the substantial technical assistance provided for drafting “the Law on Innovative Start-ups in Albania”, approved by the Albanian Parliament in 2022, and “the National Strategy for Scientific Research, Technology, and Innovation (NSSTI) 2022-2030”, approved by the government of Albania in September 2023.
ProSEED and EU4I programmes contribute to broader development goals in Albania by stimulating economic growth, creating employment opportunities, fostering innovation, supporting the digital economy and society in Albania with a special focus on skills; which are key priorities for the country's development agenda.
Could you share any lessons learned or best practices from the joint implementation of the ProSEED 2.0 and EU4INNOVATION projects?

Practitioners' Network visit to EU4Innovation project
As highlighted during the site visits in both MFC Kamza and Polis University, there are a number of projects powered and jointly implemented by the ProSEED and EU4I project teams. At the core of these projects lies the fact that educational institutions, be they VTCs/VET centres or universities, support the third mission of these institutions, which is enhancing skills and generating knowledge that benefits the social, cultural, and economic development of the country. Some of these best practices/highlight projects are:
-
ConnectIT: provides technical assistance to selected MSMEs for the digitalisation of their business processes. The project utilises the expertise of academia/IT students to support the digital transformation efforts of MSMEs. The supported MSMEs successfully adapt business models, concepts, and structures to the new market conditions and become more resilient, sustainable and future proof. Complementarily, the digitalisation of selected business processes presents a hands-on opportunity for IT oriented students (with a background or experience in digital marketing, web development, software engineering, data management, cyber security, artificial intelligence etc.) to understand the digital needs of businesses, to apply their IT skills in practice by developing real-life digital solutions for MSMEs challenges.
-
INNOVET [Innovation in VET] project aims to elevate the quality of VET programs, equip students and educators with practical skills, promote innovation and sustainability, and amplify the impact and recognition of Construction School in Korça (CSK). The aim of the project is to address specific educational and skill development needs within the CSK vocational education and training (VET) institution in Korça. It is implemented by a consortium of Junior Achievement of Albania, Polis University and the Construction School in Korça -VET school.
-
Innovation Factory (IF) is an interdisciplinary unit within Polis University that seeks to support researchers, students, young creators, entrepreneurs and businesses to innovate. At the intersection of design, technology and entrepreneurship, IF operates conceptually by generating technical expertise and knowledge in and for the ecosystem, and as a physical space offering opportunities for digital prototyping and fabrication through its latest 3D printing and scanning technologies. IF has been established with the support of EU4Innovation (Sida and GIZ) allowing students, researchers, start-ups and young makers to design, experiment and fabricate their own models and prototypes, bringing together industry and academia through a mix of teaching, learning and doing (triple helix). IF & Polis university together with the Polytechnic university of Tirana, have been implementing partners of S.E.A.M - Space for Experiments in Art and Manufacturing, a program focused primarily on the symbiotic relationship between concept and matter in terms of design, functionality and production; key to the Creative Industries. The first programme S.E.A.M & cohort of creatives is supported by EU4Innovation.
How do the projects align with the priorities of the Practitioners' Network for European Development Cooperation?
 Practitioners´ Network visit to ProSEED 2.0. projectThe projects align with the priorities of the Practitioners' Network for European Development Cooperation by focusing on innovation, research and development, technology transfer, and fostering collaboration between different stakeholders, which are key areas of interest for the Network.
Practitioners´ Network visit to ProSEED 2.0. projectThe projects align with the priorities of the Practitioners' Network for European Development Cooperation by focusing on innovation, research and development, technology transfer, and fostering collaboration between different stakeholders, which are key areas of interest for the Network.
Share: